How Do I Cycle A New Aquarium?
So, you’ve finally set up your brand-new aquarium, and now you’re wondering how to get it ready for its future inhabitants.
The process of cycling a new aquarium is crucial as it establishes a healthy ecosystem for your fish and other aquatic creatures.
In this article, we will discuss the step-by-step guide on how to cycle a new aquarium, ensuring a safe and thriving environment for your underwater friends.
Why is cycling important?
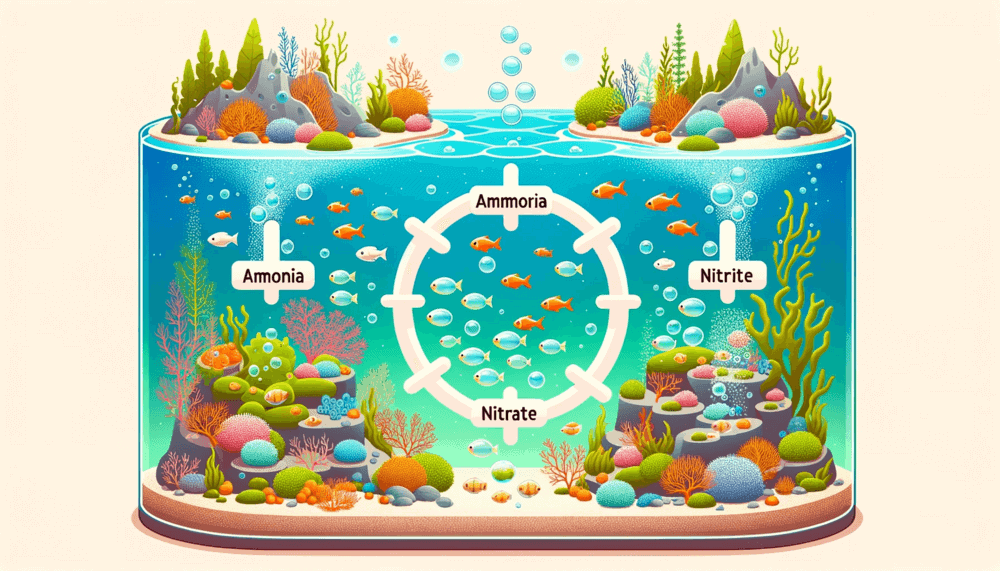
Introduction to the nitrogen cycle
Cycling a new aquarium is a crucial step in creating a healthy and thriving aquatic environment.
It involves establishing a balanced ecosystem by cultivating beneficial bacteria that convert harmful chemicals into less toxic substances.
This process, known as the nitrogen cycle, plays a vital role in maintaining water quality and ensuring the well-being of the fish and other inhabitants of the aquarium.
The importance of cycling a new aquarium
Cycling a new aquarium is essential for several reasons.
Firstly, it establishes a stable and healthy environment that supports the life of the fish and other organisms.
Without proper cycling, the water in the aquarium can become polluted with toxic ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates, leading to stress, disease, and even death of the inhabitants.
Secondly, cycling allows beneficial bacteria to colonize the aquarium, creating a natural and self-sustaining filtration system that helps maintain water quality in the long run.
Finally, cycling reduces the need for frequent and extensive water changes, as the beneficial bacteria break down waste products, making the water cleaner and safer for the aquatic life.
Preparing the aquarium
Choosing the right size
When setting up a new aquarium, selecting the appropriate size is crucial.
A larger tank generally provides a more stable environment as it has a higher water volume, which helps dilute toxins and maintain consistent water parameters.
Additionally, larger tanks offer more swimming space for the fish and allow for a greater variety of aquatic plants and decorations, creating a visually appealing and natural-looking habitat.
Selecting the appropriate tank equipment
Investing in high-quality tank equipment is essential for the overall success of your aquarium.
Filters, heaters, and lights are among the key equipment needed. Research the specific requirements of the fish species you plan to keep to determine the appropriate filtration system.
Heaters are essential to maintain the optimal temperature for the fish, while lights are necessary for plants to perform photosynthesis.
Ensure that the chosen equipment is suitable for the size of your aquarium and meets the needs of the inhabitants.
Adding substrate and decorations
Choosing the right substrate and decorations not only enhances the visual appeal of the aquarium but also provides a functional and comfortable environment for the fish.
Substrate options, such as gravel, sand, or planted substrates, should be selected based on the species of fish and plants you intend to keep.
Decorations, such as rocks, driftwood, and live plants, not only provide hiding spots and territories for the fish but also contribute to the overall health and well-being of the aquarium’s ecosystem.
Initial setup
Setting up the filtration system
Setting up a reliable filtration system is critical for maintaining optimal water quality.
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to assemble and install the filtration system correctly.
It is advisable to use a combination of mechanical, chemical, and biological filtration methods to remove debris, chemicals, and harmful waste from the water.
Ensure that the filter media, such as foam pads or bio-balls, are clean and properly positioned within the filter compartments to maximize their effectiveness.
Adding water and treating it
Before adding water to the aquarium, it is crucial to treat it properly to make it safe for the fish.
Use a water conditioner specifically designed for aquarium use to remove harmful chlorine, chloramine, and heavy metals that may be present in tap water.
Follow the dosage instructions carefully to ensure the water is treated adequately. Slowly add the treated water to the tank to prevent disturbing the substrate and decorations.
Installing the heater and thermometer
Maintaining a consistent water temperature is essential for the well-being of the fish.
Install a reliable aquarium heater that is appropriate for the size of your tank and the temperature requirements of the fish species you plan to keep.
Place the heater near the water flow to ensure proper heat distribution. Attach a thermometer to the side of the aquarium to monitor the water temperature regularly.
This will help identify any fluctuations and allow for timely adjustments if necessary.
Introducing beneficial bacteria
Understanding the role of beneficial bacteria
Beneficial bacteria play a crucial role in the nitrogen cycle by converting harmful ammonia, produced from fish waste and uneaten food, into nitrites and subsequently into nitrates.
These bacteria, known as nitrifying bacteria, colonize the filter media, gravel, and other surfaces in the aquarium.
The establishment of a robust population of beneficial bacteria is vital to ensure the efficient removal of toxic substances and maintain a healthy aquatic environment.
Using seeding material or established media
To kick-start the colonization of beneficial bacteria, it is beneficial to use seeding material or established media from an existing, well-established aquarium.
This material contains a high concentration of nitrifying bacteria that will aid in the cycling process. It can be obtained from a local fish store or borrowed from a fellow aquarium enthusiast.
Place the seeding material, such as sponge, filter media, or gravel, into your new aquarium’s filter chamber to introduce the beneficial bacteria.
Opting for bacterial supplements
In addition to using seeding material, another option to introduce beneficial bacteria is by using bacterial supplements.
These products contain specially formulated strains of nitrifying bacteria that are designed to accelerate the establishment of a healthy nitrogen cycle.
Follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer to dose the aquarium with the appropriate amount of bacterial supplement.
Be patient during this process, as it can take several weeks for the bacteria to fully establish and begin effectively converting ammonia and nitrites.
Monitoring ammonia levels
Testing for ammonia
Monitoring ammonia levels is crucial during the cycling process to ensure the establishment of a healthy nitrogen cycle.
Test kits specifically designed for measuring ammonia levels in aquariums are readily available.
Follow the instructions provided with the test kit to accurately measure the ammonia concentration in the water.
Regular testing, especially during the first few weeks of cycling, will help track the progress and identify any potential ammonia spikes.
Reacting to ammonia spikes
Ammonia spikes can occur during the initial stages of cycling, which can be detrimental to the health of the fish. If ammonia levels rise above acceptable limits, it is vital to take immediate action to reduce the toxicity.
Perform partial water changes, replacing a portion of the water with treated and temperature-matched water, to dilute the high ammonia concentrations.
Additionally, ammonia detoxifiers can be used to temporarily neutralize ammonia and provide some relief for the fish.
Be vigilant and monitor the ammonia levels closely to ensure they remain within tolerable ranges.
Partial water changes and ammonia detoxifiers
Regular partial water changes are an effective way to maintain water quality and manage ammonia levels in the aquarium.
Aim to replace approximately 20% of the water every one to two weeks, depending on the size of the aquarium and the number of inhabitants.
By replacing a portion of the water, you are diluting any accumulated ammonia and removing other unwanted substances.
Additionally, using ammonia detoxifiers, which temporarily bind and neutralize ammonia, can be beneficial during the cycling process and in emergency situations.
Tracking nitrite levels
Testing for nitrites
Once beneficial bacteria have established and started converting ammonia, another toxic substance, called nitrite, will begin to accumulate.
Nitrite is also harmful to fish and can cause stress and illness if present in high concentrations. Test kits specifically designed for measuring nitrite levels in aquariums are readily available.
Regularly test the water using these kits to monitor the nitrite concentrations.
Dealing with nitrite spikes
Similar to ammonia spikes, nitrite spikes can occur during the cycling process. If nitrite levels rise above safe limits, prompt action is necessary to protect the fish.
Perform partial water changes, replacing a portion of the water with treated and temperature-matched water, to dilute the nitrite concentrations.
Additionally, nitrite-neutralizing products, available at pet stores, can be used temporarily to reduce the toxicity. Monitor the nitrite levels closely and take steps to ensure they remain at manageable levels.
Partial water changes and nitrite-neutralizing products
Continuing to perform regular partial water changes, even after the initial cycling phase, is essential for maintaining healthy water conditions and managing nitrite levels.
Partial water changes help dilute nitrite concentrations and remove other waste products accumulating in the aquarium.
Alongside water changes, nitrite-neutralizing products can provide additional support in emergency situations where nitrite levels rise suddenly and pose a threat to the well-being of the fish.
Measuring nitrate levels
Testing for nitrates
As the nitrogen cycle progresses, the nitrifying bacteria convert nitrite into nitrate, which is less toxic than ammonia and nitrite but can still be harmful at high concentrations.
Test kits designed specifically for measuring nitrate levels in aquariums are widely available.
Regularly testing the water for nitrate concentrations will help maintain an optimal level that is safe for the fish and other inhabitants.
Managing nitrate build-up
To manage nitrate build-up, regular water changes are essential.
By replacing a portion of the water with fresh, treated water, you dilute the accumulated nitrates, reducing their concentration in the aquarium.
Aim to perform partial water changes of approximately 20% every one to two weeks, depending on the nitrate levels and the needs of the inhabitants. Additionally, incorporating live plants into the aquarium can help absorb nitrates as they perform photosynthesis, contributing to a healthier and more balanced ecosystem.
Controlling nitrates through regular water changes
Regular water changes, combined with proper filtration and maintenance, are effective ways to control and maintain nitrate levels in the aquarium.
By replacing water on a consistent basis, you reduce the accumulation of nitrates and prevent them from reaching harmful concentrations.
Alongside water changes, having live plants in the aquarium can aid in the natural removal of nitrates. Monitoring nitrate levels regularly and taking appropriate action will help ensure a healthy and thriving aquatic environment.
Maintaining stable pH levels
Monitoring pH regularly
Maintaining a stable pH level is crucial for the overall health and well-being of the fish.
pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of the water and can impact the fish’s ability to respire, digest food, and ward off diseases.
Regularly test the aquarium’s pH using a reliable pH test kit. The optimal pH range for most freshwater fish is typically between 6.5 and 7.5.
By monitoring pH regularly, you can detect any fluctuations or imbalances and address them promptly.
Adjusting pH if necessary
If the pH level deviates from the ideal range for the fish species you intend to keep, you may need to adjust it.
This can be achieved through various methods, such as using pH-adjusting chemicals or utilizing buffering agents.
It is essential to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer and make gradual adjustments to avoid sudden pH swings, which can be harmful to the fish.
When adjusting pH, consider the specific needs of the fish species and aim to create a stable and suitable environment for them.
Utilizing buffering agents and conditioners
Buffering agents and conditioners can be valuable tools in maintaining stable pH levels in the aquarium. These products help stabilize and regulate the pH, preventing drastic fluctuations that can stress the fish.
Some buffering agents are specifically designed for freshwater aquariums and can be used to adjust the pH gradually. Additionally, conditioners that contain pH stabilizers can be used during water changes to minimize disruptions to the pH balance.
Proper use of these products, in conjunction with regular monitoring, will help ensure a stable and suitable pH level for the inhabitants.
Introducing a living organism
Choosing the right fish or other inhabitants
After the aquarium has been cycled and water parameters are stable, it is time to introduce the first living organisms.
Choosing the right fish or other inhabitants is crucial for the long-term success of the aquarium. Research the specific requirements of the species you are interested in, including their compatibility with other fish and their environmental needs.
Consider factors such as size, behavior, and water temperature requirements to ensure the inhabitants can coexist harmoniously and thrive in their new habitat.
Acclimating the new organism
Before adding the new organism to the aquarium, proper acclimation is essential to minimize stress and help them adjust to the water conditions.
Float the sealed bag containing the fish or other organism in the aquarium water for approximately 15-20 minutes to allow the water temperature to equalize. Afterward, open the bag and gradually add small amounts of aquarium water into the bag at regular intervals over the course of about an hour.
This slow mixing of water helps the organism gradually acclimate to the new environment.
Avoiding overcrowding and adding slowly
To maintain a healthy and balanced ecosystem, it is crucial to avoid overcrowding the aquarium. Overpopulation can lead to increased waste production, elevated stress levels, and potential aggression among the inhabitants.
When adding new fish or other organisms, introduce them slowly, allowing time for the aquarium to adjust to the increased bio-load.
Monitor the behavior and water parameters to ensure the existing inhabitants are not overwhelmed by the new additions.
By taking a cautious approach and allowing the aquarium to establish a natural balance, you increase the chances of maintaining a thriving and harmonious aquatic environment.
Continued monitoring and maintenance
Testing water parameters regularly
Even after the initial cycling phase and the addition of the fish or other inhabitants, it is crucial to continue monitoring the water parameters regularly.
Perform routine tests for ammonia, nitrite, nitrate, and pH levels to ensure they remain within acceptable ranges. Regular testing, typically once a week, will help you detect any changes or imbalances that may require intervention.
By staying proactive in monitoring the water parameters, you can address any issues promptly and maintain a healthy and stable aquatic environment.
Performing routine maintenance
Routine maintenance is vital for the ongoing health and longevity of the aquarium.
Regularly clean the glass, remove debris from the substrate, and trim any excess vegetation to keep the aquarium visually appealing and functioning optimally. Additionally, clean or replace filter media as necessary to maintain its efficiency and prevent the accumulation of harmful substances.
Check and adjust the heater, filter, and other equipment regularly to ensure they are functioning correctly. By adhering to a consistent maintenance schedule, you promote a clean and healthy environment for the inhabitants.
Ensuring a healthy and balanced ecosystem
To ensure a healthy and balanced ecosystem, it is necessary to maintain a consistent and diligent approach to aquarium care. Provide a suitable habitat for the inhabitants by monitoring and adjusting water parameters, performing routine maintenance, and providing appropriate nutrition.
Observe the behavior of the fish and other organisms regularly, looking for any signs of stress, illness, or aggression. Address any issues promptly and seek assistance from knowledgeable sources, such as aquarium professionals or online communities, when needed.
By investing time and effort into the ongoing care of your aquarium, you create an environment where the inhabitants can thrive and bring you joy for years to come.
In conclusion, cycling a new aquarium is a crucial step in creating a healthy and thriving aquatic environment.
By following the proper steps in preparing the aquarium, introducing beneficial bacteria, and regularly monitoring water parameters, you can establish a stable and balanced ecosystem.
Taking the time to choose the right inhabitants and providing them with appropriate care and maintenance will result in a beautiful and rewarding aquarium that brings delight to both you and the aquatic life within it.
So, embark on your journey to cycle a new aquarium with enthusiasm and enjoy the wonders of the aquatic world.
